What is Seborrheic Dermatitis? – Exploring the Causes, Symptoms, and Triggers of This Common Skin Condition
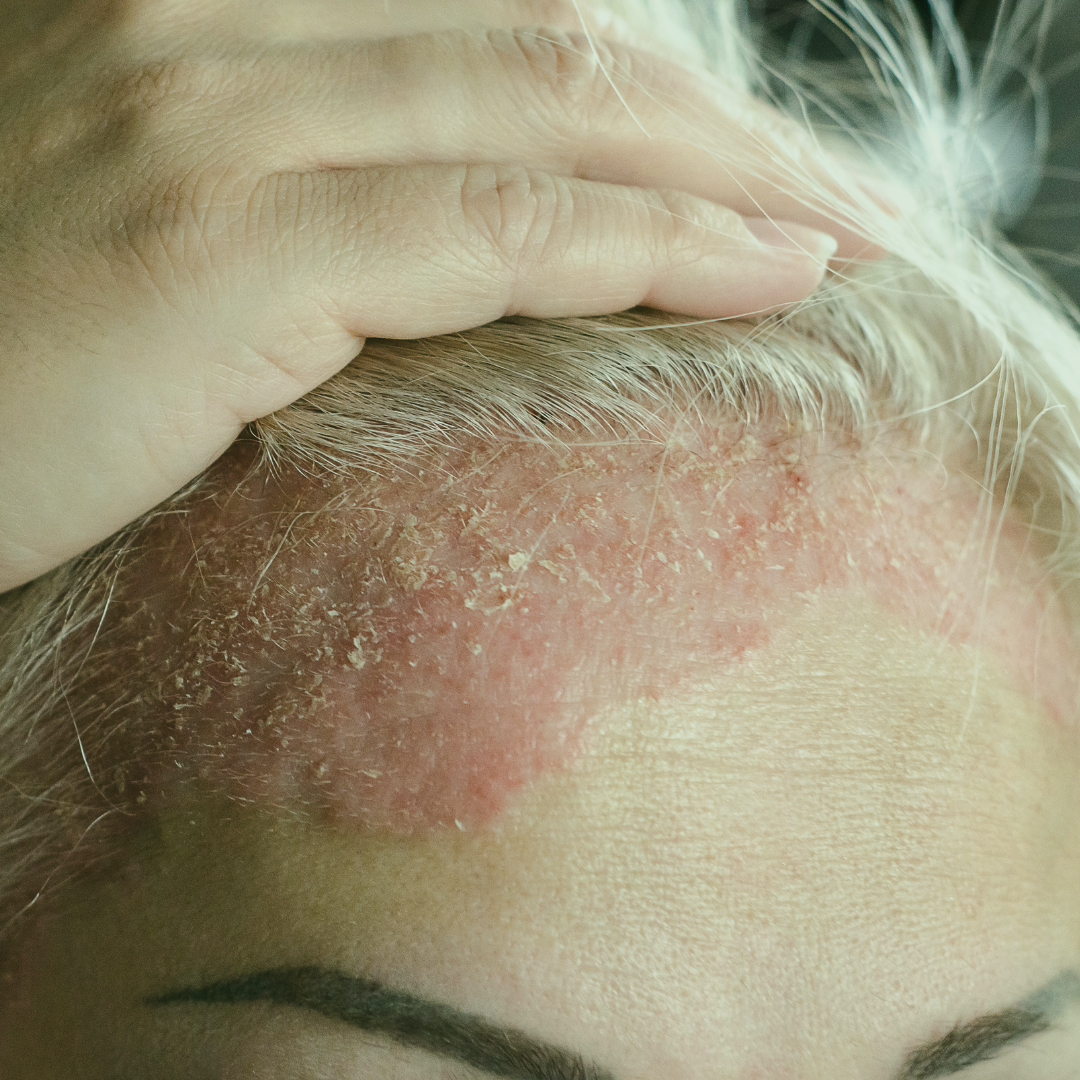
Seborrheic dermatitis (SD) is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects areas rich in sebaceous (oil) glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. Characterized by red, scaly, and often itchy skin, it is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis remains unclear, it is believed to involve a combination of factors such as genetics, environmental influences, and the overgrowth of yeast on the skin. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and triggers of seborrheic dermatitis is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis
The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development.
- Overproduction of Sebum: Sebaceous glands produce an oily substance called sebum, which helps keep the skin hydrated. However, in seborrheic dermatitis, the overproduction of sebum can lead to an oily scalp and provide a breeding ground for yeast growth.
- Malassezia Yeast: Malassezia, a type of yeast that naturally occurs on the skin, is thought to play a role in seborrheic dermatitis. In individuals with SD, this yeast can overgrow, triggering an inflammatory response that leads to the characteristic redness and scaling.
- Genetics: A genetic predisposition may also play a role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis. Individuals with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it.
- Immune System Dysfunction: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, Parkinson’s disease, or other chronic conditions, are at a higher risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis. The immune system’s inability to regulate the inflammatory response may contribute to more severe cases.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly during periods such as puberty or pregnancy, can exacerbate seborrheic dermatitis. This may explain why the condition is more prevalent in young adults and tends to improve with age.
- Climate Factors: Cold, dry weather can trigger flare-ups, while hot, humid conditions can also contribute to symptom severity. The condition tends to worsen during the winter months when the air is dry and exposure to sunlight is reduced.
Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis can present differently in various individuals, but common symptoms include:
- Red, scaly patches: The skin develops red or pink patches that are often covered in greasy, white, or yellow scales.
- Itching: Itching is a common symptom, particularly on the scalp, and can sometimes be severe.
- Flaking: Flaking of the skin, especially on the scalp, is a hallmark of seborrheic dermatitis. This can appear similar to dandruff, though SD flakes are often larger and oilier.
- Oily, inflamed skin: The affected areas may appear greasy or oily, with inflamed patches of skin. On the scalp, this can lead to thick, crusted plaques.
- Cradle Cap in Infants: Seborrheic dermatitis can also affect infants, where it is known as cradle cap. It presents as thick, crusty patches on the baby’s scalp, but it usually resolves without treatment by the time the child is one year old.
Seborrheic dermatitis most commonly affects the scalp but can also occur on the face, especially around the nose, eyebrows, eyelids, and behind the ears. In more severe cases, it can spread to the upper chest and back.
Triggers of Seborrheic Dermatitis
While seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic condition, several factors can trigger or worsen flare-ups:
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress is a well-known trigger for seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups. High levels of stress can weaken the immune system and increase the severity of symptoms.
- Cold Weather: As previously mentioned, cold, dry climates can exacerbate seborrheic dermatitis, causing flare-ups during the winter months when the skin is more prone to dryness.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can trigger seborrheic dermatitis in susceptible individuals.
- Use of Harsh Skin Products: Soaps, shampoos, and skincare products containing alcohol, strong fragrances, or harsh chemicals can irritate the skin and trigger seborrheic dermatitis.
- Medical Conditions: Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease or HIV/AIDS, are more prone to developing seborrheic dermatitis due to compromised immune systems.
- Diet and Nutrition: Although the connection between diet and seborrheic dermatitis is not well established, some people report that certain foods, particularly those high in sugar and processed fats, can worsen their symptoms.
Managing Seborrheic Dermatitis
Managing seborrheic dermatitis typically involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, skincare, and medications. Over-the-counter treatments, such as medicated shampoos containing ingredients like ketoconazole, zinc pyrithione, or selenium sulfide, are effective in managing scalp symptoms. For more severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe stronger antifungal creams, corticosteroids, or other medications to control inflammation.
Maintaining a regular skincare routine is also essential. Using gentle cleansers, avoiding hot water, and moisturizing regularly can help manage symptoms and reduce the likelihood of flare-ups. It’s important to avoid picking or scratching affected areas, as this can worsen inflammation and increase the risk of infection.
Conclusion
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common, chronic skin condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. While the exact cause is not fully understood, several factors, including yeast overgrowth, genetic predisposition, and environmental triggers, contribute to its development. Managing seborrheic dermatitis often requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, topical treatments, and regular skincare routines.
If you suspect you have seborrheic dermatitis or are experiencing persistent symptoms, it is essential to consult with a dermatologist. Early intervention can help manage the condition effectively and prevent complications.
For more detailed information on seborrheic dermatitis, visit the American Academy of Dermatology’s official website or check the National Eczema Association’s resources on seborrheic dermatitis.
References
- Mayo Clinic. “Seborrheic Dermatitis.” Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
- American Academy of Dermatology. “Seborrheic Dermatitis.” Retrieved from https://www.aad.org
- National Eczema Association. “Seborrheic Dermatitis.” Retrieved from https://nationaleczema.org





