What is Scalp Psoriasis? An Introduction to the Condition, Causes, and How it Affects the Scalp
Scalp psoriasis is a common yet often misunderstood chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a type of psoriasis—a long-lasting autoimmune disease—that predominantly affects the scalp. For many, the condition can be both physically uncomfortable and emotionally challenging, impacting daily life. This article will provide an in-depth look at scalp psoriasis, including its causes, how it affects the scalp, the symptoms, and common triggers for flare-ups.
What is Scalp Psoriasis?
Scalp psoriasis occurs when skin cells multiply faster than normal, leading to the formation of thick, scaly patches on the scalp. This excessive skin cell production is caused by an overactive immune system, where the body mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow and shed over a period of weeks, but in individuals with scalp psoriasis, this process happens over days, leading to the accumulation of skin cells on the surface of the scalp.
These patches can be isolated to one small area or cover the entire scalp. In some cases, scalp psoriasis can extend to the forehead, neck, and even behind the ears. While the exact cause of scalp psoriasis is unknown, it is believed to be influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Those with a family history of psoriasis or other autoimmune conditions are at a higher risk.
Symptoms of Scalp Psoriasis
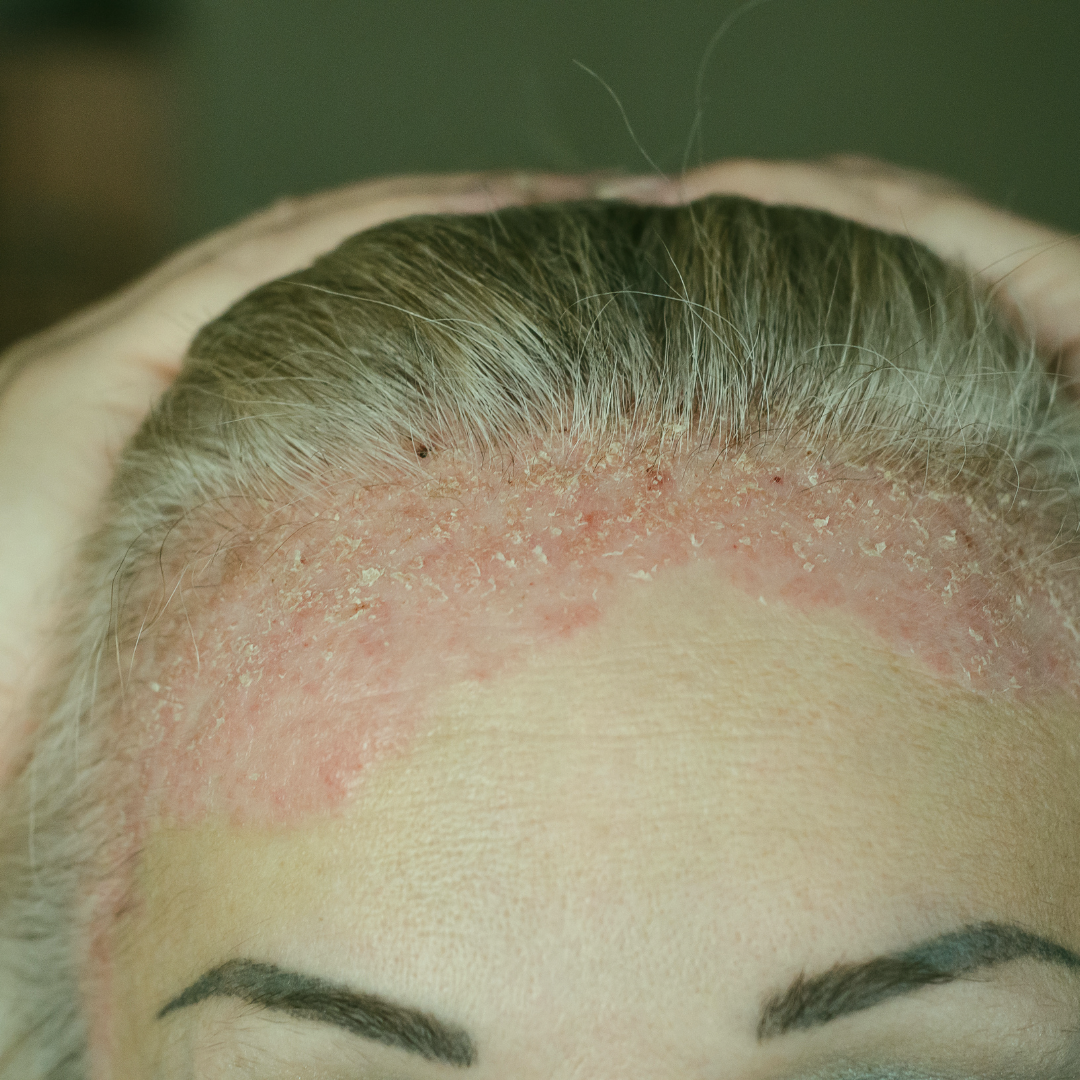
One of the most noticeable symptoms of scalp psoriasis is the appearance of thick, silvery-white scales or plaques on the scalp. These plaques are often accompanied by redness and inflammation. Below are common signs and symptoms to watch out for:
- Red Patches on the Scalp: The skin on the scalp becomes inflamed, resulting in red or pinkish patches. These patches can vary in size and may become tender.
- Flaking: The scalp may appear similar to dandruff, but the flakes associated with scalp psoriasis are typically thicker and more persistent. The white, silvery flakes often accumulate, making the scalp feel dry and itchy.
- Itching and Irritation: The itching associated with scalp psoriasis can range from mild to severe. In extreme cases, constant scratching can cause the scalp to bleed or become infected, worsening the condition.
- Dry Scalp: The scalp often feels dry and tight due to the buildup of dead skin cells.
- Burning or Soreness: Some individuals experience a burning sensation or soreness, especially during flare-ups.
- Hair Loss: While scalp psoriasis itself doesn’t directly cause hair loss, excessive scratching and inflammation can lead to temporary hair thinning or shedding. Fortunately, hair usually grows back once the psoriasis is under control.
Scalp psoriasis can be easily confused with other conditions like seborrheic dermatitis (commonly known as dandruff) due to the flaking. However, psoriasis flakes are typically thicker, and the affected areas are more defined compared to dandruff, which is often more diffuse and greasy.
Common Triggers of Scalp Psoriasis Flare-ups
Like many autoimmune conditions, scalp psoriasis can go through periods of remission and flare-ups. Understanding what triggers these flare-ups is key to managing the condition. Below are some common triggers that can worsen scalp psoriasis:
- Stress: Emotional and psychological stress is one of the most common triggers of psoriasis flare-ups. Stress can lead to the release of chemicals in the body that aggravate inflammation and immune response, leading to increased symptoms.
- Infections: Certain infections, particularly streptococcal throat infections or skin infections, can trigger a flare-up of scalp psoriasis. These infections stimulate the immune system, which in turn worsens the autoimmune response in psoriasis.
- Cold, Dry Weather: Cold temperatures and dry air tend to dry out the skin, which can aggravate psoriasis symptoms. In contrast, warm weather and sun exposure can often help alleviate symptoms, though too much sun can also trigger a flare.
- Skin Injuries (Koebner Phenomenon): Even minor injuries to the skin, such as cuts, scrapes, or burns, can trigger new patches of psoriasis in those areas. This is known as the Koebner phenomenon, where any skin trauma leads to psoriasis development.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, like beta-blockers (used to treat high blood pressure) or lithium (used to treat mood disorders), can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. If you are taking any medications and notice a worsening of symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider.
- Alcohol and Smoking: Both alcohol consumption and smoking are associated with worsening psoriasis symptoms. Smoking can directly affect immune function, while alcohol can increase inflammation, both of which can trigger flare-ups.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can lead to an increase in psoriasis symptoms. Many women experience flare-ups during pregnancy, though some report symptom relief.
Managing Scalp Psoriasis
While there is currently no cure for scalp psoriasis, many treatment options are available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatments include:
- Topical Treatments: Medicated shampoos containing coal tar or salicylic acid are often recommended. Steroid creams or ointments may also help reduce inflammation.
- Light Therapy: Phototherapy, or UV light treatment, is another option that can help slow skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
- Systemic Medications: In more severe cases, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed to suppress the immune system and reduce symptoms.
It’s also important to adopt a daily scalp care routine that includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and avoiding triggers like stress and injury to the scalp.
For more detailed information, check reputable sources such as the National Psoriasis Foundation and the American Academy of Dermatology, which provide comprehensive guides on living with scalp psoriasis.
Conclusion
Scalp psoriasis is a manageable condition, but it requires proper diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan to control flare-ups and maintain a healthy scalp. If you suspect that you may have scalp psoriasis, it’s important to consult with a dermatologist who can guide you through treatment options and help you minimize its impact on your life.












